Design and Manufacture of Memristor Chips for Artificial Intelligence
Introduction
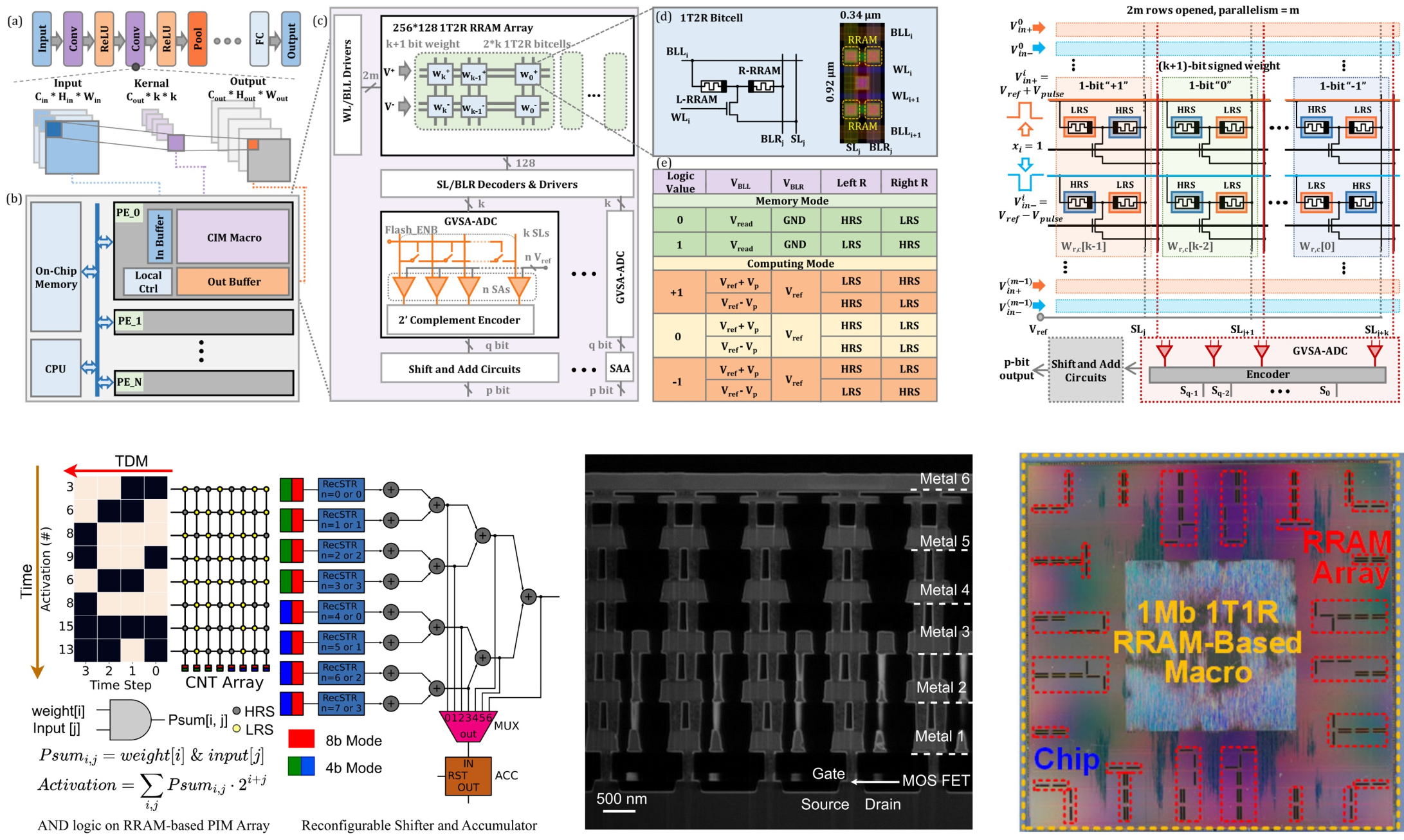
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, the number of parameters and computation of advanced algorithmic models represented by deep learning is surging year by year, which poses a new challenge to the traditional computing hardware platforms based on the von Neumann architecture. Focusing on the need for big computing power and high energy efficiency in intelligent applications at the edge and big data applications in the cloud, our group is committed to the study on design of high-efficiency memory circuits, high-performance analog-to-digital converter circuits, advanced operator accelerators, multi-core network-on-chip architectures, compression and local efficient deployment of advanced algorithmic models with respect to the memristor-based compute-in-memory chips for artificial intelligence. We have been working closely with foundries for a long time, and the research results have been published in the top journals in the field of chip design, such as JSSC and TCAS-I.
Neuromorphic Devices and Brain-Inspired Computing
Introduction
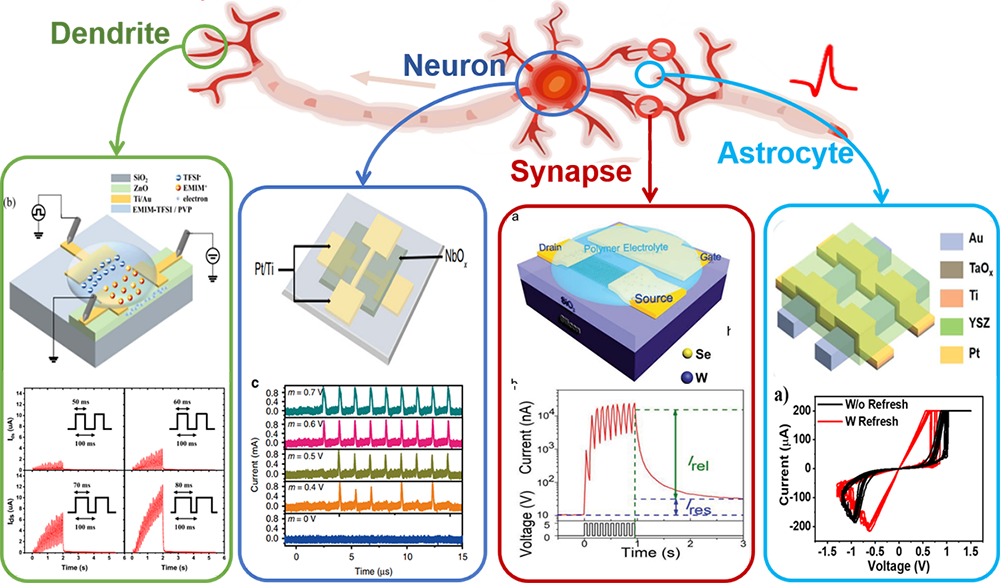
Based on metal oxides, a material system rich in complex ionic dynamics, thermal and electrical effects and coupling effects, our group has developed a variety of artificial neuromorphic devices, which can efficiently complete various bionic tasks and brain-like computing. Through careful design of the proportions of various components in the resistive materials and the geometry of the device, we can realize a variety of complex biological nervous system behaviors in small-scale nanodevices. The devices that have been designed, manufactured and functionally verified include: NbOx neurons with behaviors such as leakage, accumulation and firing; ZnO-EMIM artificial dendritic devices with long- and short-term plasticity at the same time; YSZ-based astrocyte devices; ultra-low-power artificial devices with power consumption of only 30fJ/spike synaptic device. Based on these novel neuromorphic devices, our group has further realized complex biological neural functions including time series analysis, associative memory and so on. Research results related to this direction have been published many times in top journals in the field, such as Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, etc.
Memristor-Based Efficient Computing System
Introduction
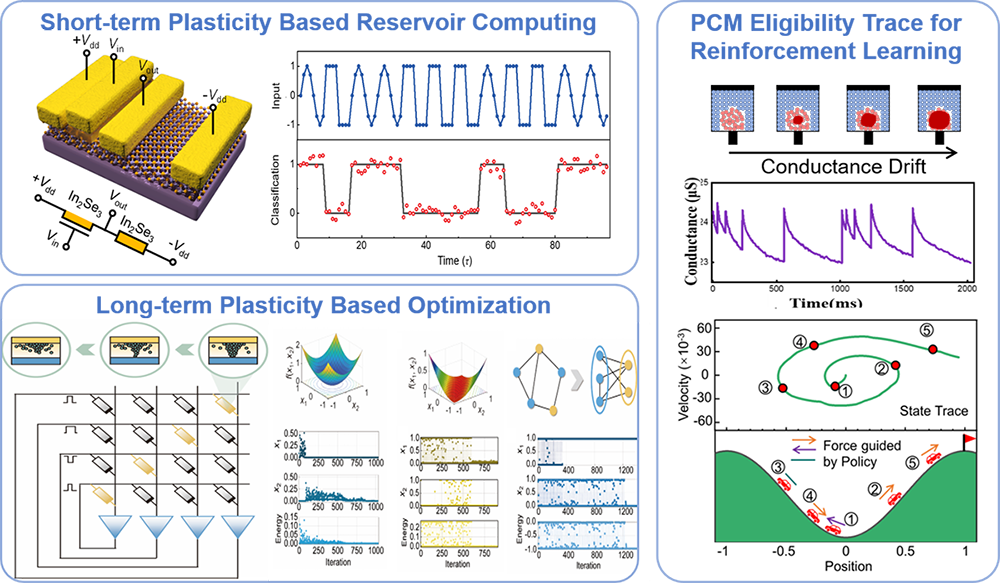
In view of the diversity of computing methods in artificial intelligence algorithms, our group combines the internal dynamic characteristics of memristors with the advantages of memristor arrays in in-memory computing, and efficiently implements a variety of expensive operations in traditional computing platforms, including random number generation, matrix-vector multiplication, matrix attenuation and so on. As a result, we have achieved extremely low power consumption in many different types of artificial intelligence hardware computing systems. The current representative systems mainly include: the reservoir computing system based on the short-term plasticity of the two-dimensional ferroelectric material α-In2Se3, which can efficiently process complex timing information with extremely low power consumption; the phase-change memory(PCM)-based eligibility trace calculation system, which can efficiently implement the eligibility trace mechanism by using the attenuation caused by PCM conductance drift and can effectively accelerate the training process of reinforcement learning; the optimization problem solving system based on long-term plasticity TaOx memristor, etc. The research results in this direction have been published many times in top journals and conferences in the field of microelectronics such as Science Advances, Advanced Materials, IEDM, etc.